Understanding Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is at the forefront of the global transition towards sustainable and environmentally friendly energy systems. It plays a crucial role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of renewable energy sources, their benefits, challenges, and the future of renewable energy.
Introduction to Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that replenish themselves faster than they are consumed. Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, renewable sources such as the sun, wind, water, and biomass are readily available. The main types of renewable energy include:
- Solar Energy (sunlight)
- Wind Energy (air movement)
- Hydropower (water flow)
- Geothermal Energy (heat from the Earth’s core)
- Bioenergy (organic materials)
As of 2024, renewable energy contributes nearly 30% of the world’s electricity supply, with countries increasingly investing in cleaner energy solutions.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
1. Solar Energy
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity or heat. The two primary methods are:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Systems – Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Solar Thermal Systems – These use mirrors or collectors to focus sunlight and generate heat for water heating or power production.
Benefits and Applications
- Clean and abundant energy source
- Can be deployed at various scales (from small homes to large power plants)
- Decreases dependency on fossil fuels
China and the U.S. lead the world in solar energy production, with the cost of solar panels decreasing significantly over the last decade.
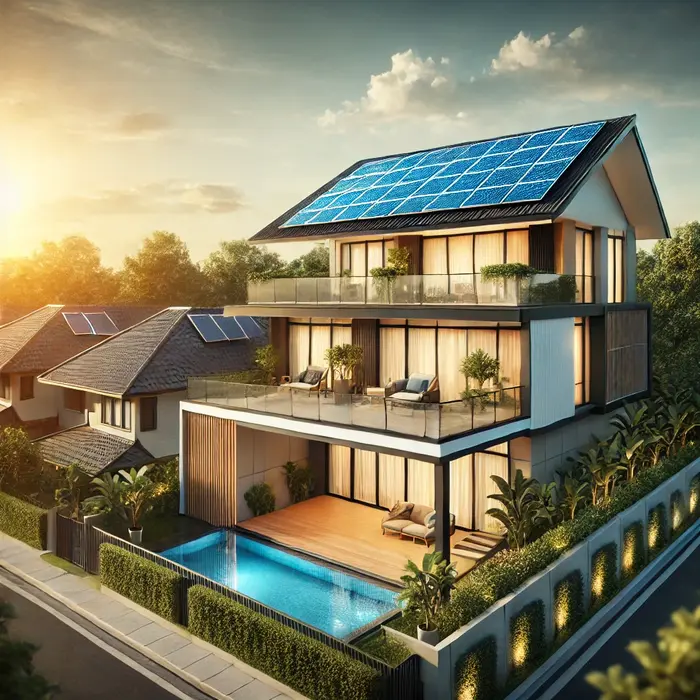


Solar Energy – A rooftop solar panel installation on a modern house.
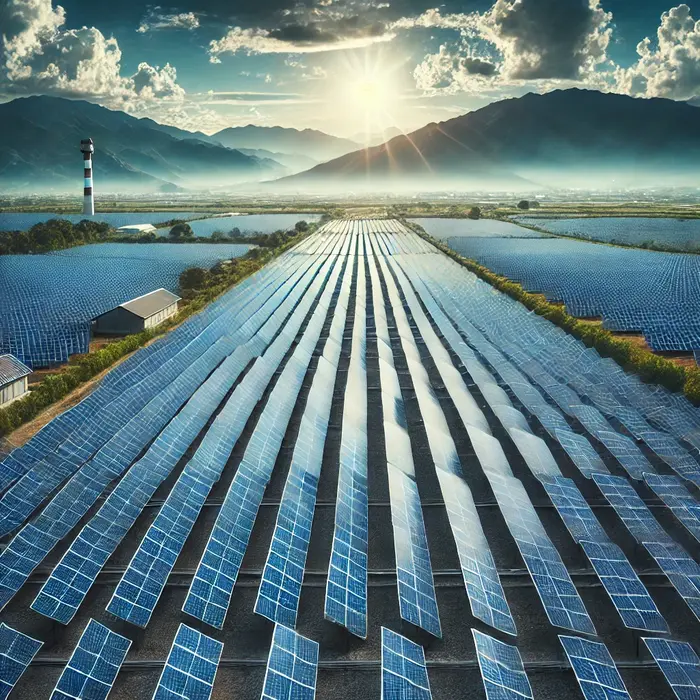
Solar Energy – A large solar farm with photovoltaic panels.
2. Wind Energy
Wind power is one of the fastest-growing energy sources globally. Large wind turbines convert wind movement into electricity.
Onshore vs. Offshore Wind Farms
- Onshore Wind Farms: Built on land, easier to install but affected by terrain and wind variability.
- Offshore Wind Farms: Located in oceans or lakes, benefiting from stronger and more consistent winds but are more expensive to construct.
Impact on Electricity Generation
Wind energy accounted for over 10% of global electricity production in 2023, with continued expansion planned in Europe and North America.
Wind energy has become a significant contributor to the global electricity supply. In 2024, renewables, including wind, accounted for 58% of the power consumed in the UK, with wind energy being the largest contributor.
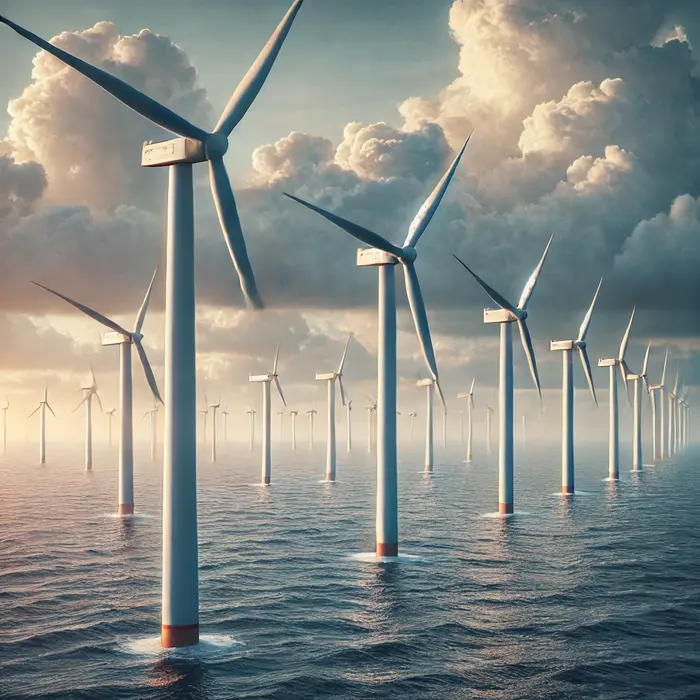


Wind Energy – An offshore wind farm with turbines in the ocean.
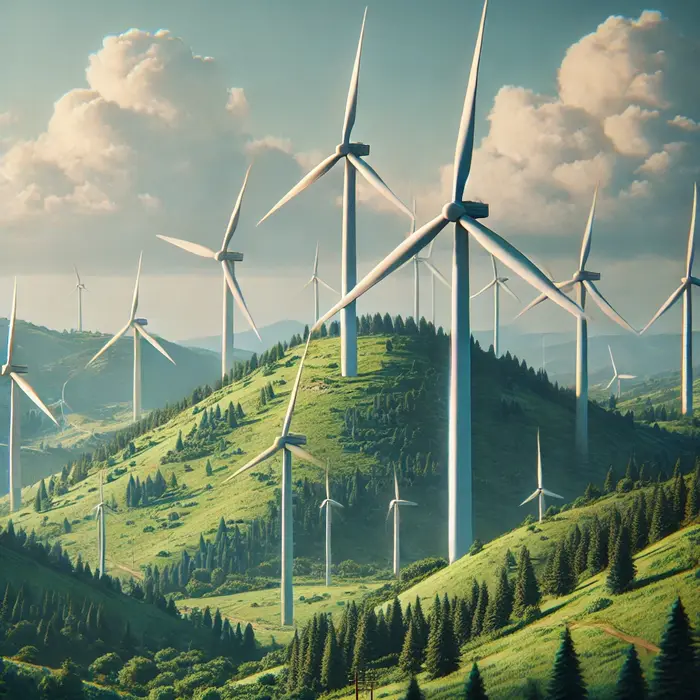
Wind Energy – A wind farm with spinning turbines.
3. Bioenergy
Bioenergy comes from organic materials, such as wood, crops, and waste. The most common forms include:
- Biomass Power Plants – Burning wood or agricultural waste to generate electricity.
- Biofuels – Liquid fuels (ethanol, biodiesel) used in transportation.
Sustainability and Benefits
- Reduces waste by utilizing organic byproducts.
- Can replace traditional fuels in many applications.
- Emits lower carbon dioxide than fossil fuels.
However, bioenergy requires responsible sourcing to avoid deforestation and food supply issues.
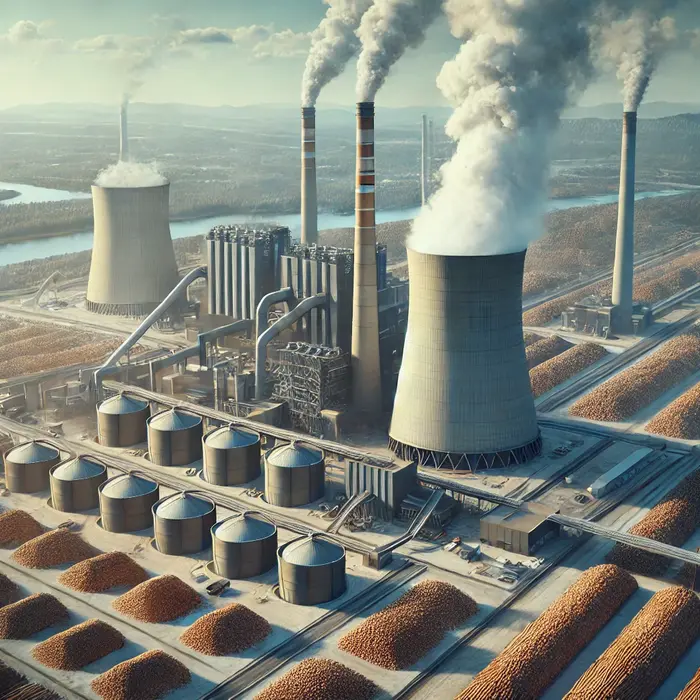


Bioenergy – A biomass power plant with organic material.
Bioenergy – A bioenergy facility processing agricultural waste into biofuels.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal power taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity or provide direct heating.
Uses and Benefits
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) can extract heat from deeper underground.
- Direct Use Applications include heating buildings, greenhouses, and hot water supply.
- Highly reliable and not dependent on weather conditions.
Iceland generates over 90% of its energy from geothermal sources, showcasing its long-term viability.
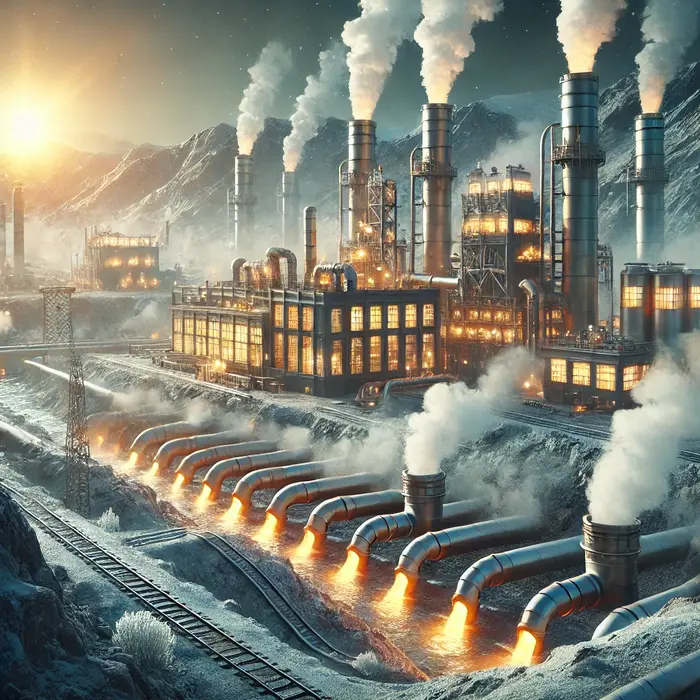
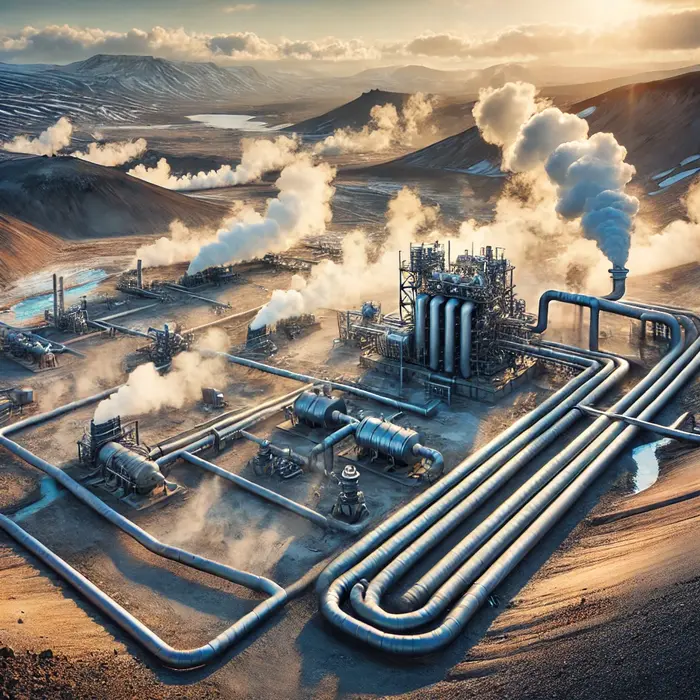


Geothermal Energy – A geothermal plant using underground heat for electricity.
Geothermal Energy – A geothermal power plant with steam rising.
5. Hydropower
Hydropower utilizes flowing water to generate electricity, with large-scale dams or small hydro stations.
Key Features and Impact
- Large-scale Hydropower: Massive dams (e.g., Three Gorges Dam in China) provide consistent power.
- Small-scale Hydropower: Ideal for rural areas with river access.
- Supplies over 16% of the world’s electricity, making it the most widely used renewable energy source.
However, hydropower dams can disrupt local ecosystems and communities.
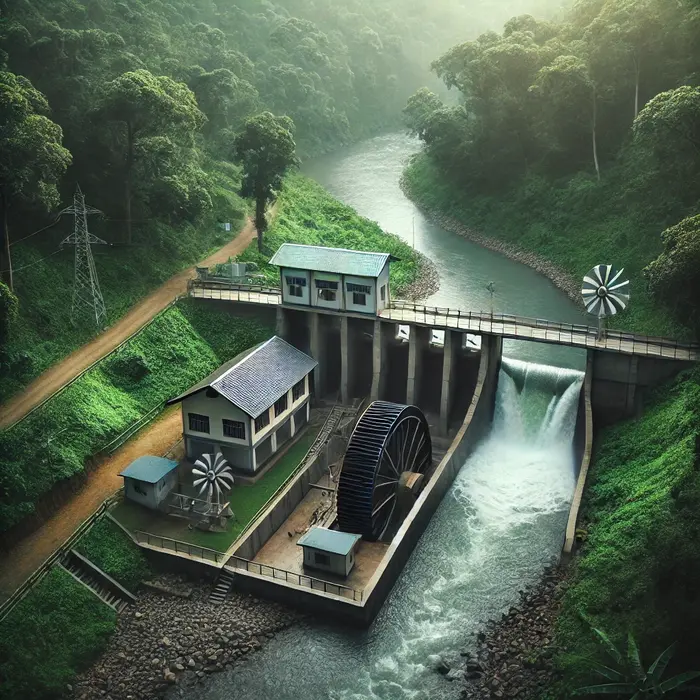
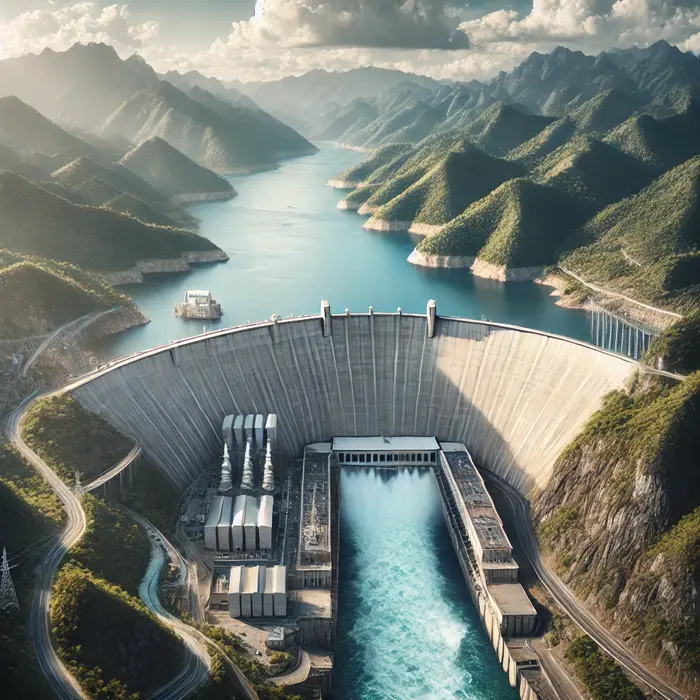


Hydropower – A small-scale hydroelectric station in a rural area.
Hydropower – A hydroelectric dam generating renewable energy.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Climate Change Mitigation
Transitioning to renewable energy is critical for reducing global carbon emissions. By replacing coal, oil, and gas with clean sources, we can:
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Improve air quality and public health
- Promote energy independence
- Reduce reliance on depleting fossil fuels
Governments worldwide aim for net-zero emissions by 2050, making renewable energy expansion essential.

A futuristic landscape featuring solar farms, wind turbines, and hydroelectric dams working together to reduce carbon emissions.
Challenges in Renewable Energy Adoption
1. Intermittency and Reliability
Renewable sources depend on natural conditions:
- Solar power requires sunlight and may not be effective in cloudy regions.
- Wind power depends on weather patterns.
- Energy storage solutions (like batteries) help manage fluctuations.
2. Economic and Policy Barriers
- Cost concerns: Although prices are decreasing, initial investment remains high.
- Infrastructure upgrades: Power grids need updates to handle renewables.
- Government support: Policies and incentives influence the pace of adoption.
Countries that implement strong green policies and financial incentives see faster renewable energy growth.
The Future of Renewable Energy
1. Technological Innovations
- Advanced Solar Panels: Higher efficiency and lightweight designs.
- Next-Gen Wind Turbines: Taller and more efficient turbines for better energy capture.
- Marine & Infrared Energy: Tidal power and Earth’s heat radiation as emerging sources.
2. Global Trends and Market Growth
- Renewables expected to generate 50% of global electricity by 2050.
- Investment in hydrogen energy as a clean fuel alternative.
- Increasing battery storage capabilities for continuous power supply.
The renewable energy sector is creating millions of new jobs, benefiting economies and communities worldwide.

A panoramic view of a sustainable city powered by renewable energy, with solar panels on rooftops, wind turbines, and a hydroelectric dam in the distance.
Conclusion on Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is no longer an option—it’s a necessity for a sustainable future. By adopting solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and bioenergy solutions, we can combat climate change, reduce pollution, and ensure a greener planet for future generations.
Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to accelerate the clean energy transition. As technology advances and costs decrease, renewables will play a dominant role in the global energy landscape.
The future is clean, green, and renewable!
FAQs
1. What is the fastest-growing renewable energy source?
Solar and wind energy are currently the fastest-growing due to rapid technological advancements and decreasing costs.
2. Are renewable energies completely eco-friendly?
While they significantly reduce emissions, some sources (like hydropower and bioenergy) can have environmental impacts if not managed responsibly.
3. Can renewable energy completely replace fossil fuels?
With improvements in storage and grid infrastructure, renewables can potentially supply most of the world’s energy needs.
4. Why is battery storage important for renewables?
Storage solutions help maintain a stable electricity supply, especially for intermittent sources like solar and wind.
5. Which countries lead in renewable energy?
China, the U.S., and the EU are leading in solar, wind, and hydropower investments, with ambitious climate targets.
Reference:
-
Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Accessed January 30, 2025. https://archive.ipcc.ch/pdf/special-reports/srren/SRREN_Full_Report.pdf
-
Renewable Energy as a Solution to Climate Change, PubMed Central. Accessed January 30, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11189203/
-
The Adoption of Renewable Energy Towards Environmental Sustainability, PubMed Central. Accessed January 30, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10994344/
-
A Review of Renewable Energy Sources, Sustainability Issues, and Climate Change Mitigation, Cogent Engineering. Accessed January 30, 2025. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23311916.2016.1167990
-
Cost, Environmental Impact, and Resilience of Renewable Energy Sources in Climate Change Mitigation, Environmental Chemistry Letters. Accessed January 30, 2025. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10311-022-01532-8