Introduction : Definition For El Niño phenomenon
The Definition For El Niño phenomenon can be understood as a natural climate event that occurs in the tropical Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by warmer than normal sea surface temperatures, and has been known to affect weather patterns across the globe. This article will discuss the history and science of El Niño, the current state of the phenomenon, and its potential effects on the environment and human activity.
History of El Niño
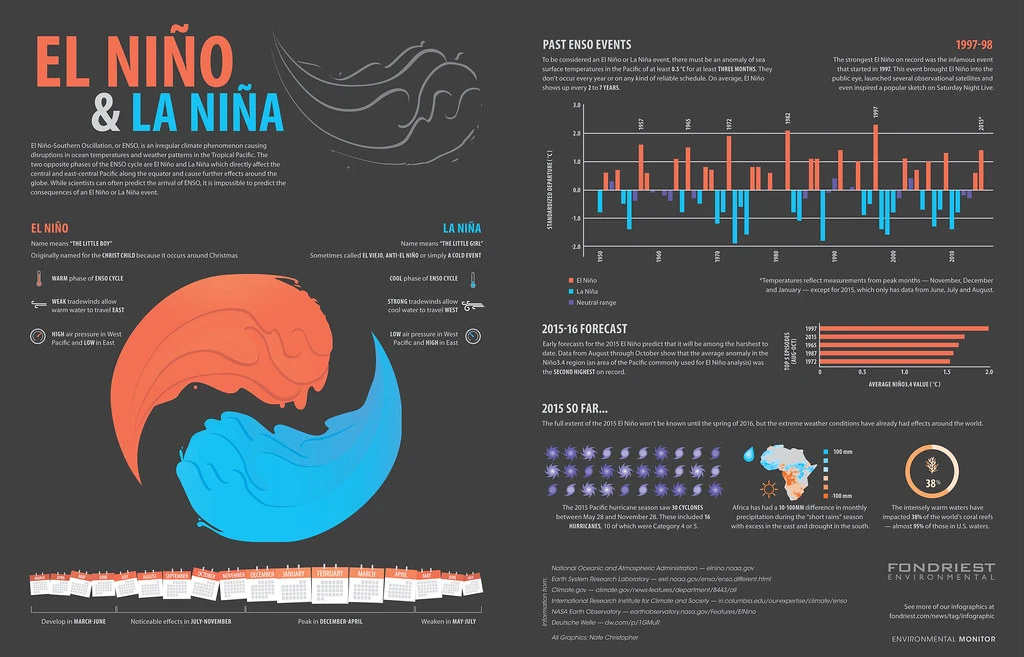
The El Niño phenomenon has been known for centuries. Fisherman off the coast of Peru noticed that the waters near them would become unusually warm and fish catches would decline around the same time every year. This phenomenon became known as El Niño and was linked to a decrease in the availability of oceanic resources.
In the 1940s, scientists began to study El Niño more closely and discovered that it was more than just a local phenomenon. They observed that El Niño was linked to changes in the atmospheric pressure of the tropical Pacific Ocean, and that the phenomenon could affect weather patterns around the world.
The Science of El Niño
El Niño is caused by the interaction between the atmosphere and the ocean in the tropical Pacific Ocean. When the ocean surface in this region is warmer than normal, the atmosphere is affected and weather patterns around the world can be altered.
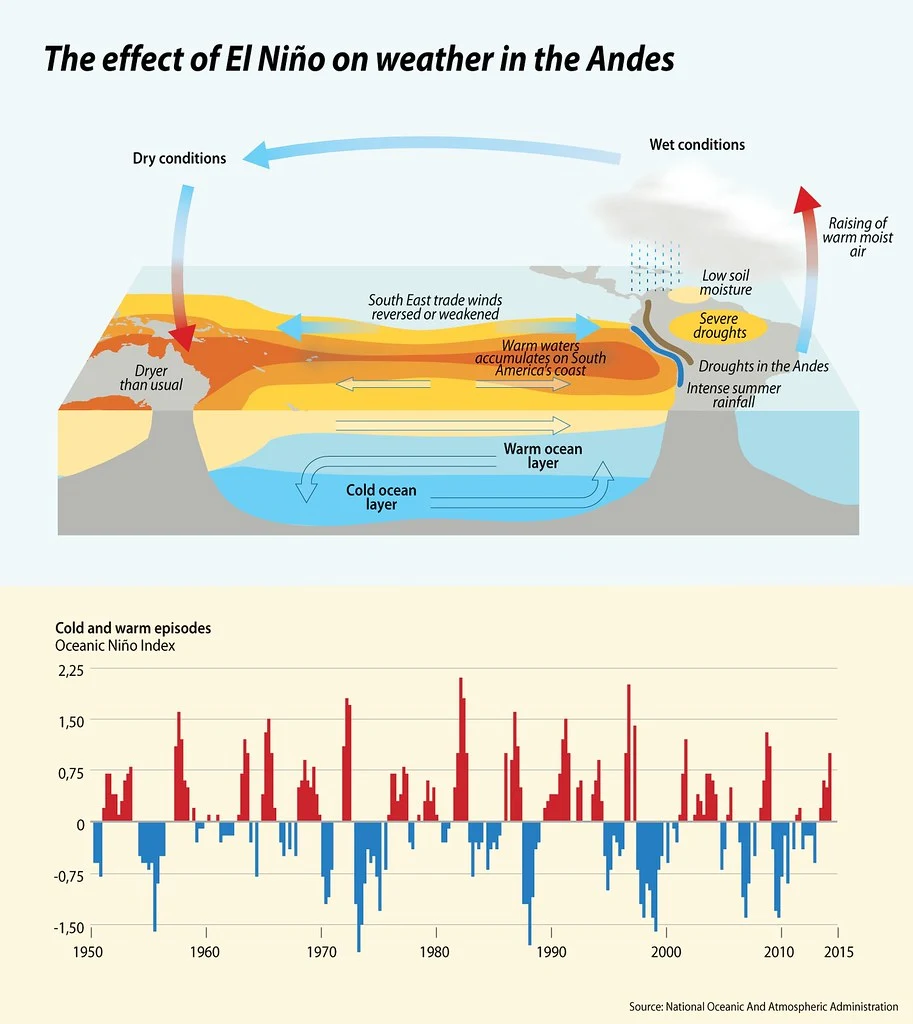
The warmer ocean temperatures during an El Niño event can cause an increase in the amount of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. This can cause the atmosphere to become unstable, leading to increased rainfall in some regions and drought in others.
Current State of El Niño
El Niño events occur on average every three to five years, and the most recent event occurred in 2015–16. The phenomenon has become more frequent and intense in recent years, and is expected to continue to do so in the future as the climate continues to change.
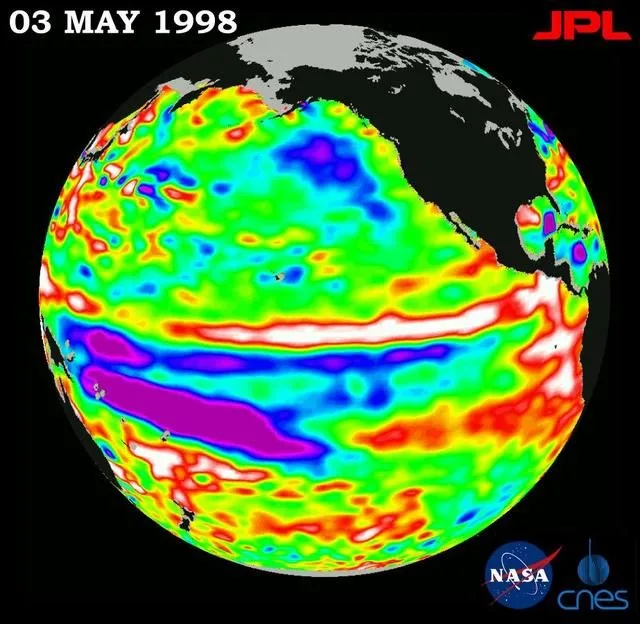
Potential Effects of El Niño
The effects of El Niño on the environment and human activity can be both positive and negative. In some regions, the increased rainfall can lead to a boost in agricultural production. In others, the drought conditions caused by El Niño can lead to famine and displacement. El Niño can also affect the amount of air pollution in certain regions. For example, increased rainfall can help to wash away air pollutants in some areas, while drought conditions can make air pollution worse in others.



Conclusion on EL Niño phenomenon
El Niño is a natural climate event that occurs in the tropical Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by warmer than normal sea surface temperatures, and has been known to affect weather patterns around the world. The history, science, current state, and potential effects of El Niño have been discussed in this article.
References
1. El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Accessed October 5, 2020. https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/teleconnections/enso/
2. What is El Niño?, National Geographic. Accessed October 5, 2020. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/global-warming/el-nino/
3. El Niño, World Meteorological Organization. Accessed October 5, 2020. https://public.wmo.int/en/our-mandate/el-ni%C3%B1o-southern-oscillation-enso